近期,我校作物纳米生物学与技术中心研究人员开发出基于二维过渡金属碳/氮化物(MXene)量子点的纳米荧光探针,并将其应用于环境水体、植物叶片和食品蔬菜中Mn(VII)、Zn(II)和草酸等物质含量的分析检测,为农业传感手段的开发和智慧作物的构建提供基础技术支持。相关研究工作以“Beyond carbon dots: Intrinsic reducibility in Ti3C2MXene quantum dots induces ultrasensitive fluorescence detection and scavenging of Mn(VII)”和“Acid-assisted ultrasonic preparation of nitrogen-doped MXene quantum dots for the efficient fluorescence “off-on-off” detection of Zn(II) in water andoxalic acid in vegetables”为题,分别在Chemical Engineering Journal和Food Chemistry期刊上发表。
MXene是一类新兴的二维层状材料,具有高比表面积、多活性位点、优异的亲水性、强吸附能力和类金属导电特性,近年在能源存储、电子器件、光电催化、膜分离和生物医学等领域应用广泛。近期研究发现,当MXene的横向尺寸减小至10 nm以下形成量子点时,由于量子限域和边缘效应的作用会使其产生光致发光现象,这一现象使得MXene量子点的设计及其在光学检测和成像标记中的应用拓展受到研究者们的关注。
研究人员在乙二胺存在条件下,通过水热处理Ti3C2MXene制备得到MXene量子点。该量子点具有还原性,能够与Mn(VII)发生氧化还原反应导致荧光猝灭,达到Mn(VII)的超灵敏检测(检测限为5.2 nM)与清除效果。进一步的实验证明MXene量子点在过氧化氢处理后会失去还原性形成碳点,该碳点能够通过内滤效应和静态猝灭过程实现对Mn(VII)的荧光响应(检测限为230 nM)。通过对比表明,MXene量子点的还原性是其能实现超灵敏检测和清除Mn(VII)的关键。该MXene量子点可应用于环境水体和植物叶片中Mn(VII)的传感与清除。
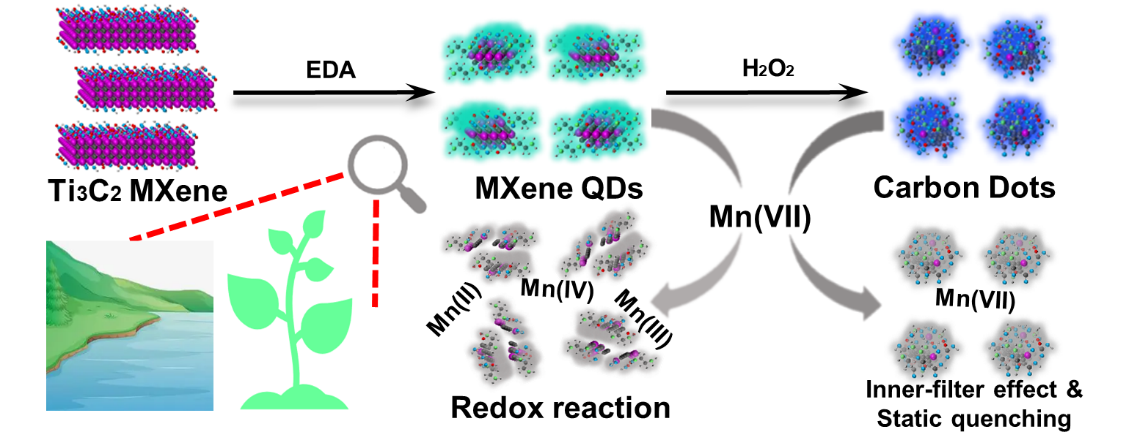
图1 MXene量子点和碳点的合成及其检测环境水体与植物叶片中Mn(VII)的机制示意图
华中农业大学化学学院教师顾江江与化学学院2020届毕业硕士研究生卢兴昌为论文的共同第一作者,顾江江与果蔬园艺作物种质创新与利用全国重点实验室、湖北省洪山实验室、植物科学技术学院吴洪洪教授为论文的共同通讯作者。该项工作得到国家重点研发计划、华中农业大学与中国农业科学院深圳农业基因组研究所合作资金资助项目、国家自然科学基金、湖北省农业科技创新中心项目和湖北省大学生创新创业训练计划项目的资助。
【英文摘要】
Recently, cutting two-dimension MXenes into quantum dots (QDs) becomes a hotspot due to the introduction of photoluminescence properties with concomitantly extensive applications. However, it is still a challenge to utilize MXene QDs (MQDs) for the simultaneous detection and scavenging heavy metal ions that may threaten environment safety and human health. Herein, MQDs are prepared by hydrothermal treatment of Ti3C2MXene in the presence of ethylenediamine and oxidized by H2O2to obtain carbon dots (CDs). These MQDs and CDs with various functional groups show excellent dispersibility, small size (less than 10 nm), good fluorescence, and high stability. Then, Ti3C2MQDs are firstly utilized to establish the fluorescent probe towards Mn(VII) with limit of detection (LOD) as low as 5.2 nM. The ultrasensitive selectivity of Ti3C2MQDs is attributed to their inherent reducibility, which can cause the redox reaction between Ti3C2MQDs and Mn(VII) with precipitous fluorescence quenching and elimination of Mn(VII). After the lack of reducibility, CDs show selective response to Mn(VII) with LOD of 230 nM based on synergistic inner-filter effect (IFE) and static quenching. Furthermore, the MQDs are successfully applied as a dual functional platform to evaluate the level of Mn (VII) and scavenge it in plant leaves. The comparation of MQDs and CDs for Mn(VII) detection and scavenging will bring more inspiration about intrinsic properties of QDs derived from MXenes for their composite material design and multifunctional use.
原文链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1385894723021769?via%3Dihub
研究者进一步开发出一种安全简单的MXene量子点合成方法。在酸及乙二胺存在条件下,通过室温超声切割多层Ti3C2MXene得到氮掺杂MXene量子点(N-MQDs)。该N-MQDs可通过荧光增强作用实现对Zn(II)特异性响应和高灵敏检测,进一步将其复合纳米结构N-MQDs/Zn(II)开发为荧光猝灭型传感器用于检测草酸。该荧光“关-开-关”型探针可应用于环境水体和食品蔬菜等实际样品中Zn(II)和草酸含量的分析。
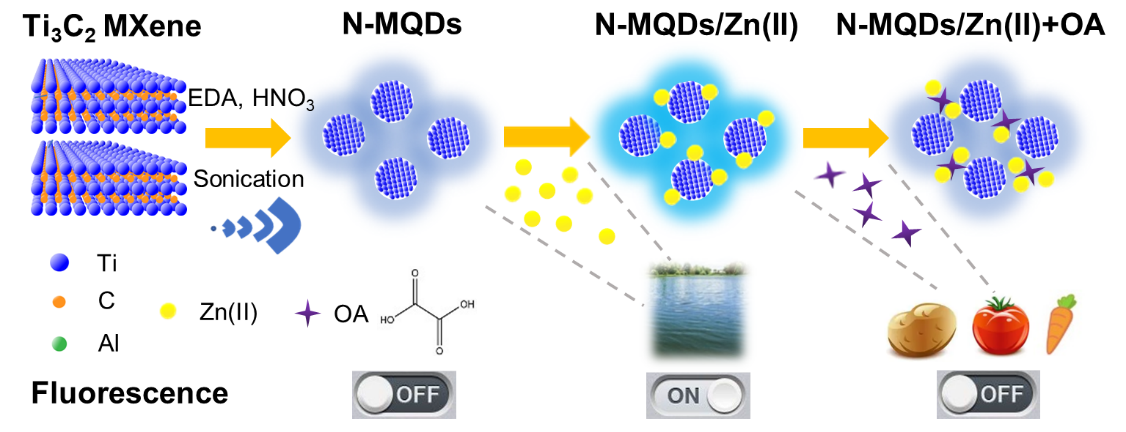
图2 超声制备氮掺杂MXene量子点及其作为荧光“关-开-关”型探针检测环境水体中的Zn(II)和食品蔬菜中的草酸示意图
华中农业大学化学学院2023届毕业硕士研究生杨锦雯为论文的第一作者,化学学院教师顾江江为论文的通讯作者,化学学院曹菲菲教授、植物科学技术学院吴洪洪教授参与了该研究的指导工作。该项工作得到国家重点研发计划、华中农业大学与中国农业科学院深圳农业基因组研究所合作资金资助项目、国家自然科学基金和湖北省大学生创新创业训练计划项目的资助。
【英文摘要】
A novel fluorescence “off-on-off” probe was presented to detect Zn(II) and oxalic acid (OA) based on nitrogen-doped MXene quantum dots (N-MQDs), which were synthesized by an ultrasound approach at room temperature with nitric acid and ethylenediamine. These N-MQDs displayed small size (<10 nm), water dispersibility, and good photoluminescence. Furthermore, the N-MQDs showed an selective response towards Zn(II) through fluorescence enhancement, with a limit of detection (LOD) calculated as 0.127 μM in the linear range of 0–20 μM. Then, the fluorescence of N-MQDs/Zn(II) system could be selectively quenched after adding OA, with an effective response in the range from 0 to 20 μM (LOD: 0.883 μM). The fluorescence “turn-on” and “turn-off” properties of N-MQDs were resulted from the intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) of Zn(II) and the coordination between OA and Zn(II), respectively. This sensing platform was successfully applied for Zn(II) and OA detection in actual environmental and vegetable samples.
原文链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0308814623016254?via%3Dihub
